Bug Reporting
Master the art of effective bug reporting with proven strategies from industry experts. Learn how to write detailed bug reports that save time and improve software quality.
Essential Resources
Explore the HTML version for enhanced visual experience
Quick Reference: bit.ly/testing_bugs - Direct link to this video content
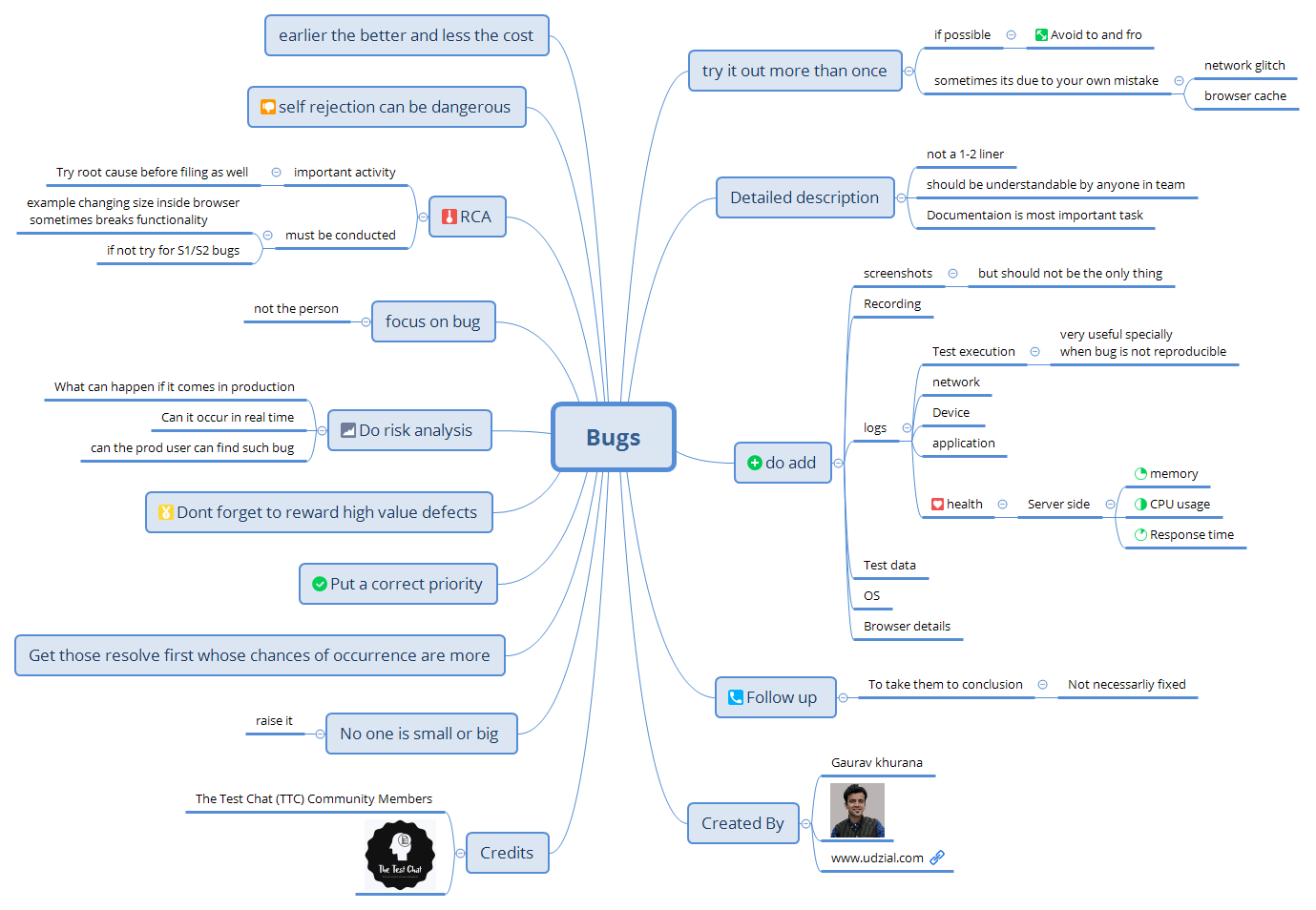
Core Bug Reporting Principles
1. Ensure Reproducibility
Before reporting any bug, ensure you can consistently reproduce it:
- Test the scenario 2-3 times to verify reproducibility
- Rule out external factors (network issues, browser cache, user error)
- Avoid unnecessary back-and-forth communication with developers
2. Write Clear, Detailed Descriptions
- Write comprehensive descriptions that any team member can understand
- Avoid one-liner bug reports
- Treat bug documentation as a critical task
3. Include Supporting Evidence
Visual Documentation
- Screenshots: Capture relevant UI elements and error states
- Screen recordings: Show the exact user flow leading to the bug
Technical Logs
- Test execution logs: Essential for non-reproducible bugs
- Network logs: Include API calls and responses
- System information: OS, browser version, device specifications
- Application logs: Error messages and stack traces
Test Environment Details
- Test data: Document exact input values used
- System configuration: Include all relevant environment settings
4. Conduct Root Cause Analysis
- Investigate potential causes before reporting
- For critical bugs (S1/S2), perform mandatory RCA
- Consider environment factors and potential impact on other features
5. Apply Risk-Based Prioritization
- Assess real-world occurrence likelihood
- Evaluate business impact and user experience effects
- Prioritize high-probability issues that users will encounter
Best Practices for Team Success
- Follow to Resolution: Track bug progress until conclusion
- Professional Communication: Focus on technical issues, not individuals
- Early Detection: Identify bugs early to reduce fix costs
- Team Culture: Encourage reporting from all team members
- Value Quality: Recognize high-impact bug discoveries
Connect and Learn More
Stay updated with testing insights and automation strategies:
- YouTube: @gauravkhurana - Testing tutorials and tips
- Medium: @gauravkhuraana - In-depth testing guides
- Topmate: 1:1 Mentoring Sessions
- Website: www.udzial.com
Acknowledgments
Thanks to The Test Chat (TTC) Community for their valuable contributions to this guide.
This guide represents collective wisdom from experienced testing professionals worldwide. Apply these practices to enhance your bug reporting skills and contribute to higher software quality.