Test Data Management in Software Testing
Effective test data management is crucial for successful software testing. This comprehensive guide covers best practices, strategies, and tools to help you create, maintain, and secure test data throughout your testing lifecycle.
🎥 Watch the Complete Guide
Watch on YouTube | Medium Article | Book 1:1 Session
Quick Reference Links
- Shortened URL: https://bit.ly/testdataintesting
This is a short way to remember the video on this page - GitHub Repository: Test Data Examples
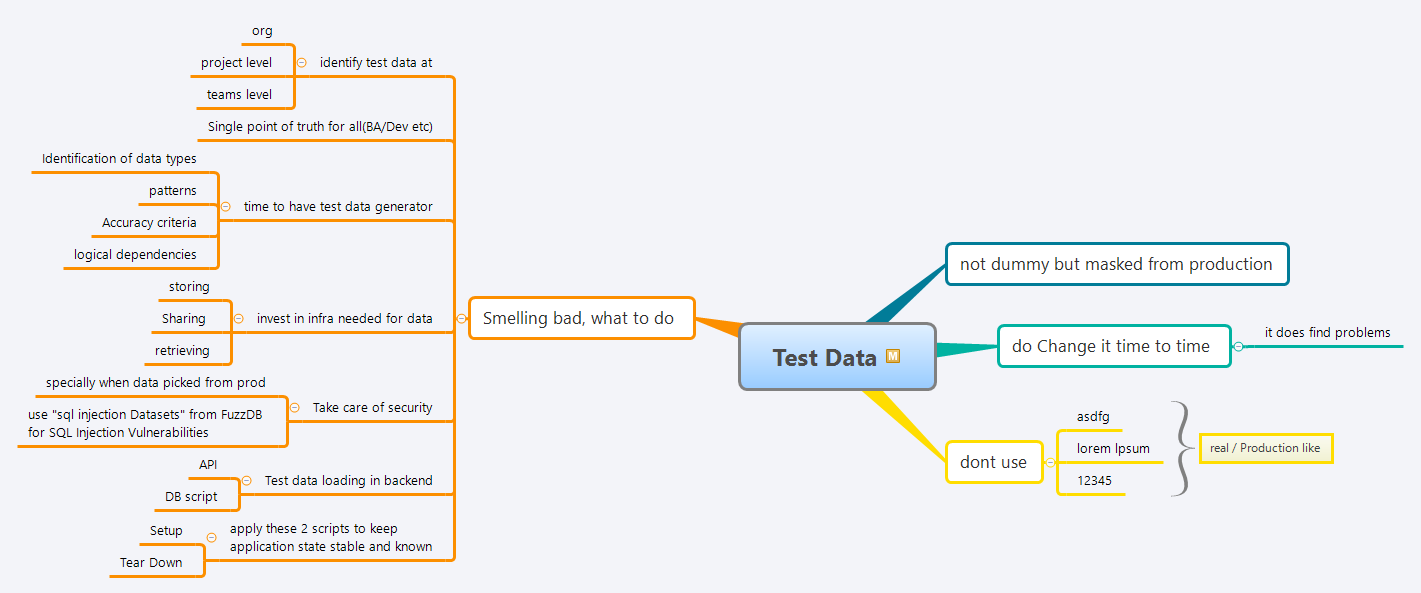
Table of Contents
- Why Test Data Management Matters
- Best Practices for Test Data
- What NOT to Use as Test Data
- Signs of Poor Test Data Management
- Test Data Strategy Implementation
- Security Considerations
- Automation and Tools
- Environment Management
Why Test Data Management Matters
Test data management is the foundation of reliable and comprehensive software testing. Poor test data leads to:
- Incomplete test coverage
- False positives and negatives
- Security vulnerabilities
- Compliance issues
- Delayed releases
Best Practices for Test Data
Use Production-Like Data (Masked, Not Real)
✅ Do: Create realistic test data by masking production data
- Maintains data relationships and patterns
- Preserves business logic constraints
- Ensures realistic testing scenarios
Keep Test Data Fresh and Updated
✅ Do: Regularly refresh your test datasets
- Prevents test data degradation
- Identifies new edge cases and scenarios
- Maintains relevance with current business requirements
- Benefits: Fresh data often reveals hidden bugs and issues
What NOT to Use as Test Data
❌ Avoid These Common Mistakes:
Real Production Data
- Risk: Data privacy violations
- Impact: Legal compliance issues
- Alternative: Use data masking techniques
Generic Placeholder Data
- Examples: "asdfg", "lorem ipsum", "12345"
- Problem: Doesn't represent real user behavior
- Impact: Misses edge cases and validation issues
Outdated Test Datasets
- Issue: Stale data doesn't reflect current business rules
- Result: Tests pass but production fails
Signs of Poor Test Data Management
Organizational Level Issues
- No standardized test data across teams
- Each team maintains separate datasets
- Inconsistent data formats and standards
Project Level Problems
- Data scattered across multiple locations
- No single source of truth
- Conflicting data versions
Team Level Challenges
- Different team members use different datasets
- No documentation of data dependencies
- Ad-hoc data creation without standards
Test Data Strategy Implementation
1. Establish Data Governance
Create a Single Source of Truth
- Centralized test data repository
- Accessible to all stakeholders (BA, Developers, Testers)
- Version controlled and documented
2. Implement Test Data Generation
Automated Data Creation
- Data Type Identification: Understand what types of data you need
- Pattern Recognition: Maintain realistic data patterns
- Accuracy Criteria: Define validation rules for generated data
- Logical Dependencies: Preserve relationships between data elements
3. Infrastructure Investment
Data Management Infrastructure
- Storage: Centralized, scalable storage solutions
- Sharing: Easy access mechanisms for all team members
- Retrieval: Fast and efficient data access methods
Security Considerations
Production Data Protection
When Using Production-Derived Data:
- Implement proper data masking techniques
- Remove or encrypt personally identifiable information (PII)
- Follow data privacy regulations (GDPR, CCPA, etc.)
Security Testing Data
Special Considerations:
- Use SQL injection datasets from FuzzDB for vulnerability testing
- Create specific datasets for security test scenarios
- Maintain separate datasets for penetration testing
Automation and Tools
Backend Data Loading
Efficient Data Management:
- API-Based Loading: Use REST/GraphQL APIs for data setup
- Database Scripts: Direct database manipulation for bulk operations
- Data Seeding: Automated data population scripts
Environment Stability Scripts
Maintain Consistent Application State:
Setup Scripts
// Example setup script structure
interface TestDataSetup {
createUsers(): Promise<void>;
seedDatabase(): Promise<void>;
configureEnvironment(): Promise<void>;
}
Teardown Scripts
// Example teardown script structure
interface TestDataTeardown {
cleanupTestData(): Promise<void>;
resetDatabase(): Promise<void>;
restoreEnvironment(): Promise<void>;
}
Environment Management
Test Environment Consistency
- Use containerization for consistent environments
- Implement infrastructure as code
- Automate environment provisioning
Data Synchronization
- Regular sync between environments
- Automated data refresh processes
- Environment-specific data configurations
Conclusion
Effective test data management is not just about having data—it's about having the right data at the right time with the right security measures. By implementing these strategies, you'll create a robust foundation for comprehensive and reliable software testing.
Key Takeaways
- Use masked production data, never real production data
- Keep test data fresh and regularly updated
- Invest in proper infrastructure and governance
- Prioritize security and compliance
- Automate data management processes
Connect & Learn More
- 📺 YouTube Channel - Testing tutorials and best practices
- ✍️ Medium Articles - In-depth testing insights
- 🎯 1:1 Mentoring - Personalized guidance
- 💼 LinkedIn - Professional updates
Remember: Great testing starts with great test data. Invest time in your test data strategy, and it will pay dividends in test reliability and software quality.