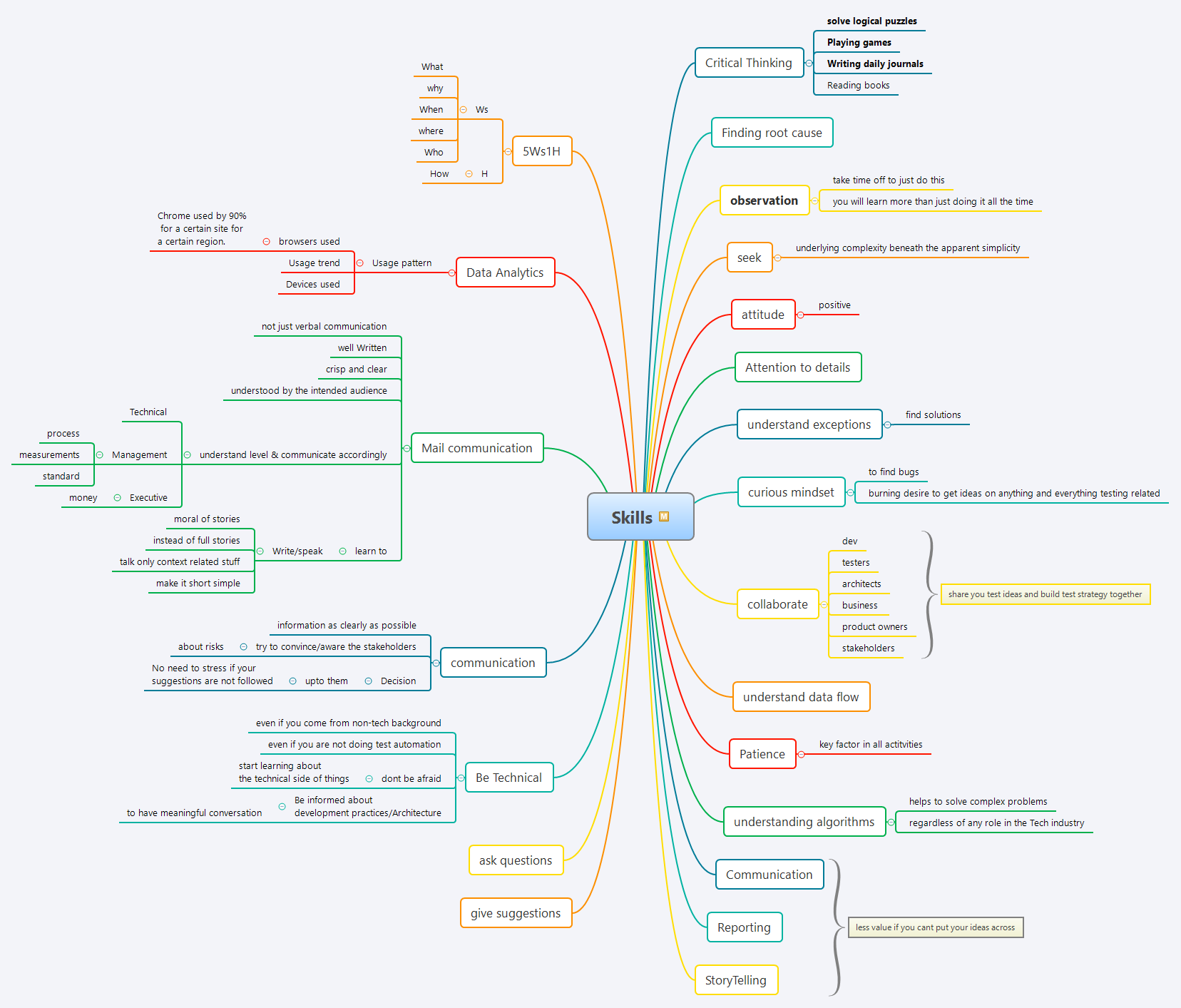
Essential Skills for Software Testers
Comprehensive guide to the fundamental skills every software tester needs to excel in their testing career and deliver quality results.
🎯 Key Resources
- Video Tutorial: Skills Required in Software Testing
- Connect with me: Topmate
📺 Video Tutorial
Watch on YouTube | Connect on Topmate | Medium Articles
💡 Core Technical Skills
1. Critical Thinking & Problem Solving
Critical thinking is the foundation of effective software testing. It enables testers to approach problems systematically and make informed decisions.
How to develop:
- Solve logical puzzles regularly
- Play strategy games that challenge reasoning
- Write daily journals to reflect on decisions
- Read books on logic and problem-solving
2. Root Cause Analysis
Understanding why issues occur is crucial for preventing future problems and improving overall software quality.
Key practices:
- Use the 5 Whys technique
- Apply fishbone diagrams for complex issues
- Document patterns in defects
- Collaborate with development teams to understand system architecture
3. Observation & Attention to Detail
Sharp observation skills help identify subtle issues that automated tools might miss.
Development strategies:
- Take dedicated time for exploratory testing
- Practice mindful observation in daily activities
- Document unexpected behaviors thoroughly
- Look for patterns and anomalies
Analytical Skills
4. Data Flow Understanding
Modern applications involve complex data interactions. Understanding these flows is essential for comprehensive testing.
Focus areas:
- API data exchange
- Database interactions
- Frontend-backend communication
- Third-party integrations
5. Algorithm Understanding
Knowledge of algorithms helps solve complex testing problems regardless of the specific technology stack.
Benefits:
- Better test case design
- Understanding of performance implications
- Improved automation strategies
- Enhanced debugging capabilities
6. Data Analytics
Understanding usage patterns helps prioritize testing efforts and identify critical areas.
Key metrics to analyze:
- Browser usage statistics (e.g., Chrome used by 90% of users in certain regions)
- Device usage trends
- User behavior patterns
- Performance benchmarks
Communication & Collaboration Skills
7. Effective Communication
Clear communication ensures that testing insights reach the right stakeholders and drive appropriate actions.
Email communication best practices:
- Write crisp and clear messages
- Adapt language to your audience:
- Technical teams: Focus on implementation details
- Management: Emphasize process improvements and metrics
- Executives: Highlight business impact and costs
- Share key insights rather than lengthy reports
- Keep context relevant and concise
8. Stakeholder Collaboration
Testing is a team effort that requires coordination with various roles.
Key collaborations:
- Developers: Share test ideas and build comprehensive test strategies
- Architects: Understand system design implications
- Business analysts: Align testing with business requirements
- Product owners: Prioritize testing based on user value
- Other testers: Knowledge sharing and peer review
9. Risk Communication
Effectively communicating risks ensures informed decision-making.
Best practices:
- Present risks clearly with supporting evidence
- Provide recommendations with pros and cons
- Respect final decisions even if they differ from your recommendations
- Focus on awareness rather than enforcement
Professional Skills
10. Reporting & Documentation
Professional reporting creates transparency and enables informed decision-making.
Key elements:
- Clear test execution summaries
- Defect reports with reproduction steps
- Risk assessments with supporting data
- Progress tracking against objectives
11. Storytelling with the 5W1H Framework
Structure your communication using the fundamental questions:
The 5 Ws:
- What: What was tested or what issue was found?
- Why: Why is this important or why did it happen?
- When: When should this be addressed?
- Where: Where in the system does this apply?
- Who: Who should be involved in the resolution?
The 1 H:
- How: How can this be resolved or implemented?
12. Technical Proficiency
Even non-technical testers benefit from understanding the technical aspects of software development.
Areas to focus on:
- Basic programming concepts
- Understanding of development practices
- System architecture awareness
- Database fundamentals
- API testing concepts
Getting started:
- Don't be intimidated by technical concepts
- Start with basics and build gradually
- Engage in technical discussions with developers
- Take online courses in relevant technologies
Mindset & Attitude
13. Curiosity & Investigation
A curious mindset drives thorough testing and continuous improvement.
Characteristics:
- Burning desire to find issues and improvements
- Interest in understanding system behavior
- Willingness to explore edge cases
- Passion for learning new testing approaches
14. Patience & Persistence
Testing requires methodical approaches and attention to detail.
Applications:
- Thorough test execution
- Detailed defect investigation
- Complex system analysis
- Long-term quality improvement initiatives
15. Positive Attitude & Adaptability
Maintaining professionalism while identifying issues is crucial for team dynamics.
Key aspects:
- Constructive feedback delivery
- Solution-oriented thinking
- Adaptability to changing requirements
- Collaborative problem-solving
Advanced Skills
16. Exception Handling Understanding
Knowing how systems handle unexpected scenarios improves test coverage.
Focus areas:
- Error handling mechanisms
- Recovery procedures
- Graceful degradation
- User experience during failures
17. Questioning & Suggestion Skills
The ability to ask the right questions and provide valuable suggestions distinguishes effective testers.
Development approaches:
- Practice asking open-ended questions
- Research before making suggestions
- Consider multiple perspectives
- Present ideas clearly and concisely
Getting Started
This comprehensive skill set might seem overwhelming, but remember:
- Start with fundamentals: Focus on critical thinking and communication first
- Build gradually: Add technical skills over time
- Practice consistently: Regular application reinforces learning
- Seek feedback: Learn from experienced professionals
- Stay updated: The testing field evolves continuously
Note: This is not an exhaustive list. The testing field continues to evolve, and new skills become relevant as technology advances.
Connect & Learn More
Creator: Gaurav Khurana
Website: www.udzial.com (Udzial means "Share")
YouTube: Subscribe for Testing Tutorials
Topmate: 1:1 Mentoring Sessions
Medium: Read My Articles
Credits
Special thanks to The Test Chat (TTC) Community Members for their valuable insights and contributions to this comprehensive guide.